Corrections:
Correction: Sirt3-mediated mitophagy protects tumor cells against apoptosis under hypoxia
Metrics: PDF 2358 views | ?
1 Center for Bioresources and Drug Discovery and School of Bioscience and Biopharmaceutics, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, China
2Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China
3Department of Pharmacology, The Penn State Hershey Cancer Institute, The Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine and Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA 17033, USA
4Department of Pathology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China
5Department of Pathology, Basic Medical School, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China
6Department of Plastic Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China
7Engineering Research Center of Cell and Therapeutic Antibody, Ministry of Education, School of Pharmacy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
8Center for Vascular and Translational Medicine, The College of Pharmacy, Central South University, Changsha 410013, China
9The Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410013, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Published: June 05, 2018
This article has been corrected: The correct figure 5A cell line T98G is given below:
The authors declare that these corrections do not change the results or conclusions of this paper.
Original article: Oncotarget. 2016; 7:43390-43400. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9717.
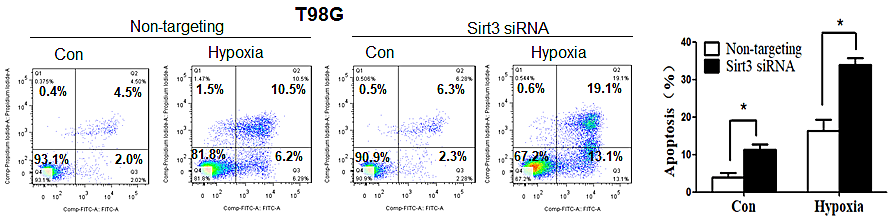
Figure 5: Suppression of Sirt3 augments the activation of apoptosis and increases the sensitivity of tumor cells to hypoxia. (A) LN229 and T98G cells were transfected with a non-targeting RNA or a siRNA targeting Sirt3, followed by hypoxia treatment for 48h. Apoptosis was determined by flow cytometric analyses of Annexin staining.
 All site content, except where otherwise noted, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
All site content, except where otherwise noted, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
PII: 25620
