The cover for issue 95 of Oncotarget features Figure 8, "Tubulin/microtubule regulation of DR5 mediated apoptosis," by Twomey, et al.
Activation of death receptor 5 to induce apoptosis in cancer cells is an attractive strategy for cancer therapy. Together, our results link the tubulin/microtubule network to the stringent regulation of DR5 mediated apoptosis, which could lead to potential therapeutic strategies to enhance cancer therapy efficacy.
Dr. Baolin Zhang from the Office of Biotechnology Products, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, at the Food and Drug Administration, in Silver Spring, MD 20993, USA said, "Death receptor-5, also known as TRAIL receptor 2, is a cell surface receptor of the TNF-receptor superfamily that contains a cytoplasmic death domain."
"Death receptor-5, also known as TRAIL receptor 2, is a cell surface receptor of the TNF-receptor superfamily that contains a cytoplasmic death domain"
- Dr. Baolin Zhang, Office of Biotechnology Products, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, at the Food and Drug Administration
Upon activation, DR5 clusters into homotrimers to assemble the adapter protein Fas-associated death domain protein and procaspase 8 or 10 into a death-inducing signaling complex, leading to activation of the caspase cascade and apoptotic execution in targeted cells .
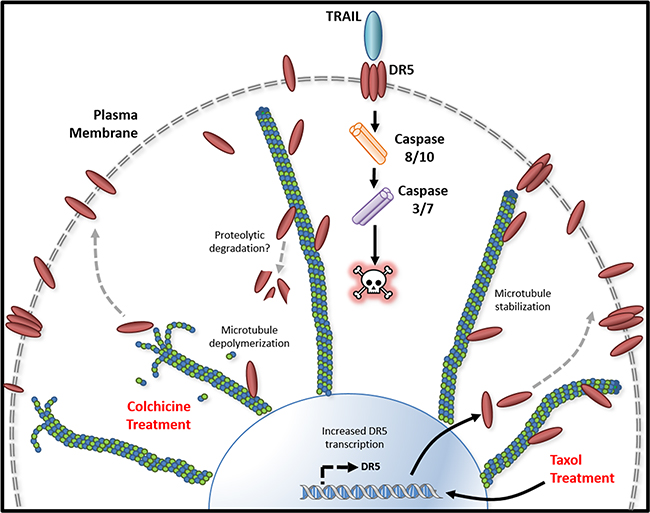
Figure 8: Tubulin/microtubule regulation of DR5 mediated apoptosis. Tubulin and DR5 are found to form stable complexes which appears to promote DR5 protein degradation via undefined pathways. Pharmacological disruption of tubulin network using either depolymerizing (e.g., colchicine) or stabilizing (e.g. taxol) agent increases DR5 total and surface expression. In both cases, the resultant cells are sensitized to TRAIL induced apoptosis. Our data suggest distinct mechanisms: 1) Tubulin depolymerization appears to lower affinity to DR5 which results in release and stabilization of DR5 protein, and 2) Tubulin stabilization shows little or effect on DR5-tubulin complex formation, but it may act via inducing DR5 transcriptional expression [21]. In either case, the upregulated DR5 protein levels may be responsible for the increased surface expression and subsequent apoptosis in response to TRAIL treatment.
In this regard, DR5 has been shown to undergo rapid internalization in a ligand-dependent manner and sequester into intracellular compartments such as the nucleus or autophagosome vesicles, leading to its absence on the surface membrane of targeted cells.
In a general scheme, apoptotic cell death is characterized by distinct morphological and biochemical changes: cell shrinkage, plasma membrane blebbing, chromatin condensation, and DNA and cells fragmentation.
Therapeutic agents targeting microtubules, including stabilizing or destabilizing agents, induce apoptosis in targeted cells and therefore are widely used for treating solid tumors and hematopoietic malignancies.
In this study, we demonstrate that tubulin interacts with DR5, leading to DR5 protein degradation in cancer cells.
The Zhang research team concluded, in their Oncotarget Research Article, "These data provide a novel mechanism by which therapeutic agents targeting tubulin/microtubules kill cancer cells. Our findings suggest that these drugs may function at least partly through upregulation of DR5 expression, leading to DR5 self-clustering and spontaneous caspase activation in targeted cells. Importantly, we showed synergistic effects of TRAIL and tubulin inhibitors to kill cancer cells. Such combinations may be able to overcome tumor resistance mechanisms, leading to better clinical outcomes in cancer patients."
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.26407
Full text - https://www.oncotarget.com/article/26407/text/
Correspondence to - Baolin Zhang - [email protected]
Keywords - tubulin, death receptor 5, TRAIL, apoptosis, cancer therapy
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a biweekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit https://www.impactjournals.com/ or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
[email protected]
18009220957x105