Oncotarget Volume 11, Issue 7 reported that to investigate the mechanisms of these oncogenic functions, the researchers performed gene expression profiling of p53 wild-type human myeloma cell lines after MAGE-A knockdown, which identified a set of 201 differentially expressed genes associated with apoptosis, DNA repair, and cell cycle regulation.
Comparative analysis of Co MMpass subjects based on high or low MAGEA3 expression revealed a set of 6748 DEG that also had significant functional associations with cell cycle and DNA replication pathways, similar to that observed in HMCL.
Dr. Hearn Jay Cho from The Tisch Cancer Institute, Icahn School of Medicine as well as The Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation said, "The type I Melanoma Antigen GEne (MAGE-A, B, and C) family has emerged as a promising new class of therapeutic targets in cancer."
"The type I Melanoma Antigen GEne (MAGE-A, B, and C) family has emerged as a promising new class of therapeutic targets in cancer."
- Dr. Hearn Jay Cho, The Tisch Cancer Institute, Icahn School of Medicine & The Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation
As their name suggests, these genes are expressed in a broad range of human cancers but in normal tissues, they are tightly restricted to developing germ cells and trophoblastic tissue.
The authors showed that several type I MAGE, particularly MAGE-A3, C1, and C2, are commonly expressed in multiple myeloma, a cancer of plasma cells, and are associated with proliferation and resistance to apoptosis.
MAGE-A3 is expressed in about 35% of newly diagnosed MM, and more, that 75% of relapsed MM cases, which is substantially higher than in most other cancers; by comparison, MAGE-A3 is expressed in about 50% of non-small cell lung cancers, 36% of melanomas, and 20% of breast cancers.
Gene expression profiling of p53 wt HMCL after MAGE-A knockdown demonstrated a set of 201 differentially expressed genes enriched for genes involved in apoptosis, DNA damage repair, and cell cycle regulation.
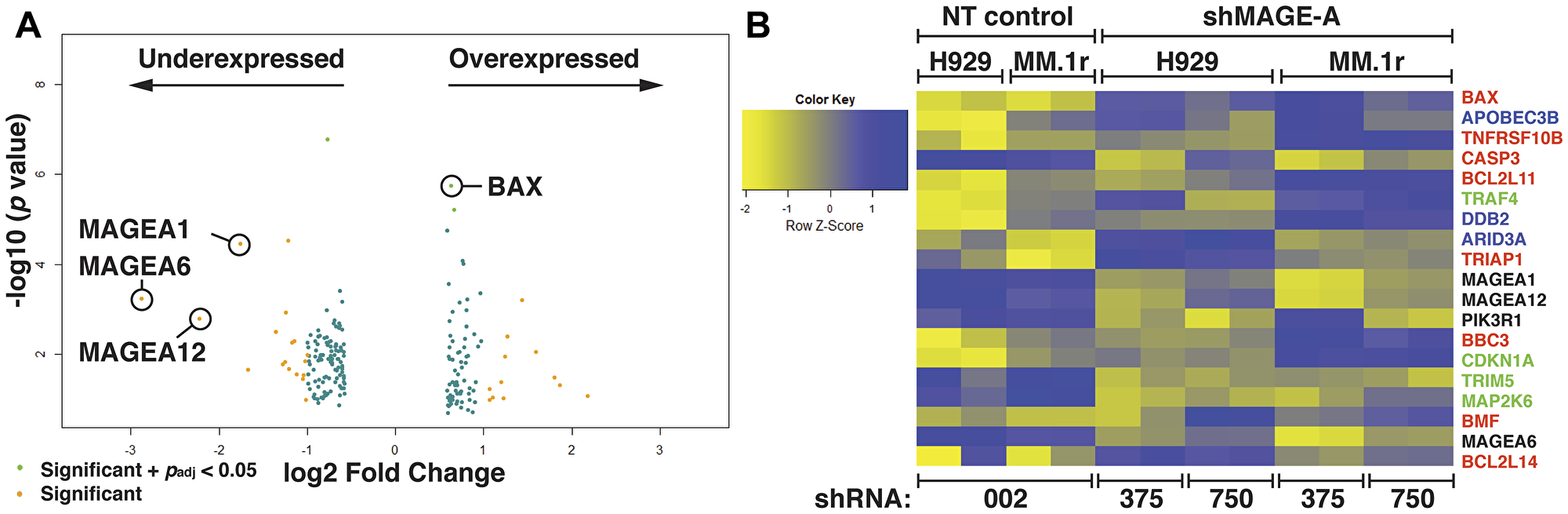
Figure 1: Gene expression profiling of HMCL after silencing of MAGE-A. (A) Volcano plot of 201 gene set with minimum 2-fold change in expression enriched from RNA seq data from MM.1r and H929 HMCL after silencing of MAGE-A by RNAi with two distinct shRNA lentiviral constructs compared to non-target control. Several MAGE-A family members are downregulated, likely reflecting direct effect of shRNA construct. Pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 genes such as BAX are among the significantly upregulated genes. Padj calculated by multiple testing using the Benjamini-Hochberg method. (B) Heat map of top over- and under-expressed genes. Apoptosis-associated genes are depicted in red. DNA-binding and repair genes are depicted in blue. Cell cycle-associated genes are depicted in green. NT, non-target shRNA lenti (SHC002, denoted as 002. shMAGE-A, MAGE-A3-targeted shRNA lenti (TRCN0000128375 and TRCN0000129750, denoted as 375 and 750, respectively).
Supervised analysis of GEP data from newly diagnosed, untreated MM patients based on MAGEA3 expression revealed significant associations with co-expression of other CTAg genes and with cell cycle and DNA replication pathways.
The Cho Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Paper that the link between DNA replication and repair, inhibition of apoptosis, and proliferation is intriguing, as very little is known about the normal function of MAGE-A in germ cell development. These results lead to the hypothesis that MAGE-A interacts with DNA repair pathways in developing germ cells to inhibit apoptosis in the setting of genome-wide double-stranded DNA breaks and resolutions. This function may also inhibit apoptosis in the setting of ongoing mutagenesis through MYC overexpression and aberrant DNA repair activity such as the APOBEC pathway, providing a pivotal role for MAGE-A in clonal evolution that is a hallmark of relapse and chemotherapy resistance in MM.
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
Full text - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27488
Correspondence to - Hearn Jay Cho - [email protected]
Keywords - MAGE-A3, multiple myeloma, apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, DNA repair
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a biweekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit https://www.impactjournals.com/ or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
[email protected]
18009220957x105