Oncotarget published "Beneficial effect of KYP-2047, a propyl-oligopeptidase inhibitor, on oral squamous cell carcinoma" which reported that This study aimed to investigate the effect of KYP-2047 in an in vitro model of TSCC and in vivo CAL27-xenograft model. Our results demonstrated that KYP-2047 was able to reduce TSCCs cell viability at the concentrations of 50 μM and 100 μM.
Additionally, KYP-2047 was able to increase Bax, Bad and caspase-3 expression, whereas Bcl-2 and p53 expression were reduced.
Moreover, KYP-2047 significantly reduced vascular-endothelial-growth-factor and endothelial-nitric-oxide-synthase expression.
In the vivo xenograft model, KYP-2047 at doses of 1 and 5 mg/kg significantly reduced tumor burden and tumor weight, decreasing also angiogenesis markers VEGF and eNOS.
Moreover, KYP-2047 increased Bax and reduced Bcl2 expressions.
Dr. Emanuela Esposito from The University of Messina said, "Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is a cancer which arises from mucosal lining of the oral cavity with strong invasion and metastasis ability."
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is a cancer which arises from mucosal lining of the oral cavity with strong invasion and metastasis ability.
Scientific evidences demonstrated that apoptosis and angiogenesis processes contribute to the development of oral cancer.
On the other hand, also angiogenesis contributes to the development of oral cancer.
Angiogenesis is a complex phenomenon that is essential for the growth and progression of solid neoplasms as oral cancer.
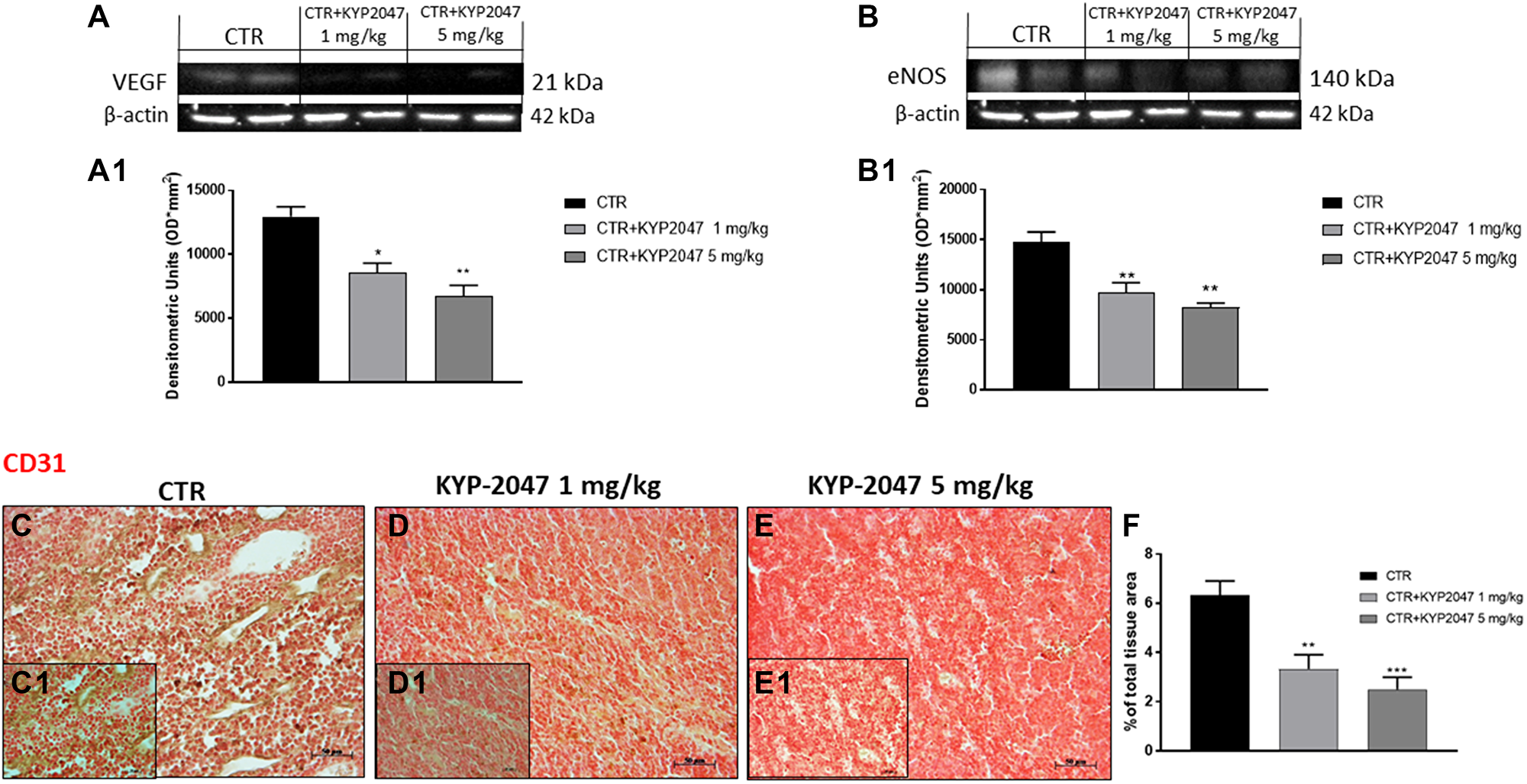
Figure 8: Effect of KYP-2047 on VEGF, eNOS and CD31 expression. The blots revealed a decrease of VEGF and eNOS expression following KYP-2047 treatment at doses of 1 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg compared to control group in a dose-dependent manner (A, A1, and B, B1). Immuhistochemical staining revealed that KYP-2047 treatment significantly reduced CD31 expression compared to control group (C, C1, D, D1, E, E1; see % of total tissue area score F). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (A) *p < 0.05 vs. CTR; **p < 0.01 vs. CTR. (B) **p < 0.01 vs. CTR. (F) **p < 0.01 vs. CTR; ***p < 0.001 vs. CTR.
Recent studies have proven the involvement of POP enzyme in cancer progression, in particular in glioblastoma, breast and gastric cancer, suggesting the development of potential POP-inhibitors as a promising strategy for cancer treatment.
Considering the fundamental role of POP in cancer pathogenesis, in the last decade several POP-inhibitors, as KYP-2047, have been developed to investigate their beneficial effect in many pathologies including cancer, showing promising results.
The Esposito Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Output, "our data demonstrated the beneficial effect of KYP-2047 for OSCC treatment, proposing that it could be an alternative therapeutic strategy to counteract oral cancer progression. However, further investigations into the involvement of KYP-2047 in oral carcinogenesis will be required to fully understand its advantageous effect."
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28147
Correspondence to - Emanuela Esposito - [email protected]
Keywords - oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC), prolyl-oligopeptidase (POP), angiogenesis, apoptosis
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a biweekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit https://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
[email protected]
18009220957x105