Oncotarget Volume 9, Issue 90 of features Figure 4, "Docking of 2HF, DNPSG and ATP to RLIP76," by Awasthi, et al.
The researchers studied 2HF in small cell and non-small cell lung cancer cell lines for sensitivity to 2HF antineoplastic activity and to determine the role of the GS-E transporter Rlip in the mechanism of action of 2HF. Binding of Rlip to 2HF was evident from successful purification of Rlip by 2HF affinity chromatography.
Results of in-vivo nude mouse xenograft studies of SCLC and NSCLC, which showed that orally administered 2HF inhibited growth of both histological types of lung cancer, confirmed in-vitro study results.
Dr. Sanjay Awasthi from the Division of Hematology and Oncology, in the Department of Internal Medicine, at Texas Tech Health Sciences Center, in Lubbock, TX 79430, USA said, "Lung cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer and the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, the most common cancer diagnosed in men with more than 1.5 million persons annually"
"Lung cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer and the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, the most common cancer diagnosed in men with more than 1.5 million persons annually"
- Dr. Sanjay Awasthi, Division of Hematology and Oncology, in the Department of Internal Medicine, at Texas Tech Health Sciences Center
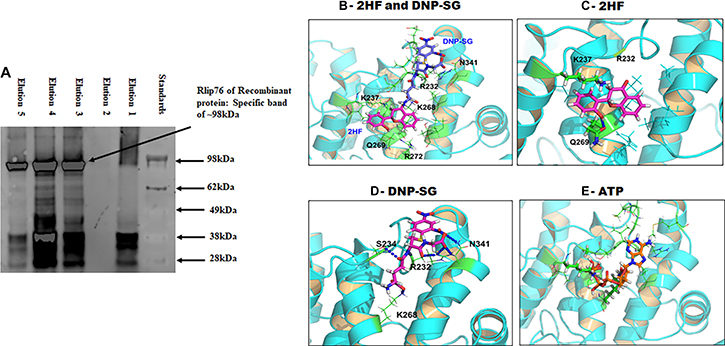
Figure 4: Docking of 2HF, DNPSG and ATP to RLIP76. (A) Binding interaction of RLIP with 2HF was demonstrated by elution of recombinant RLIP with elution buffer containing 2HF. (B) shows binding modes of 2HF and DNP-SG at the R232 site. (C) 2HF forms a hydrogen bond with Q269 and cation-π interaction with K237. (D) DNP-SG forms hydrogen bond/salt bridge network with R232/S234/K268/N341. (E) ATP also prefers binding at the ATP-binding pocket of Rlip forming 5 H-Bonds to G235, K237, S265, K268 and R272. Details are given in the Materials and Methods section.
Lung cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer and the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, the most common cancer diagnosed in men with more than 1.5 million persons annually.
TP53 is mutated in 94%, of small cell lung cancer, 94% of squamous, and 54% of adenocarcinoma subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer.
The dual role of GSTs in cancers, ameliorating carcinogenic mutations but protecting mutated cells from undergoing apoptosis may be a reason for failure of many antioxidants in lung cancer prevention trials.
Early lung cancers have previously not been readily detectable at an early curable stage, the effectiveness of low-dose antioxidants in lung cancer prevention could be underestimated by inclusion of patients with preclinical malignancy.
We studied the effects of 2HF in lung cancer cell lines and found that 2HF displays strong anticancer activity in both small cell and non-small cell histologies of lung cancer associated and present evidence of direct interaction of 2HF with Rlip.
Reductions of cyclin B-CDK1 complex levels are related to cell cycle arrest at G2 and finally DNA fragmentation."
The Sanjay Awasthi research team concluded, in their Oncotarget Research Article, "In addition to inhibiting the PIK3CA/AKT/p70S6K pathway that promotes the growth of cells, we found the cell cycling and proliferation were also affected, as evidenced by reduction in CCNB1 and CDK4 protein."
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.26329
Full text - https://www.oncotarget.com/article/26329/text/
Correspondence to - Sanjay Awasthi - [email protected]
Keywords - 2'-hydroxyflavanone, lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, Ralbp1
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a biweekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit https://www.impactjournals.com/ or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
[email protected]
18009220957x105